In mining, construction and aggregate processing, roller crushers and jaw crushers are widely used but often confusing for selection. This article simplifies their key differences to help you decide.

hydralic roller crusher
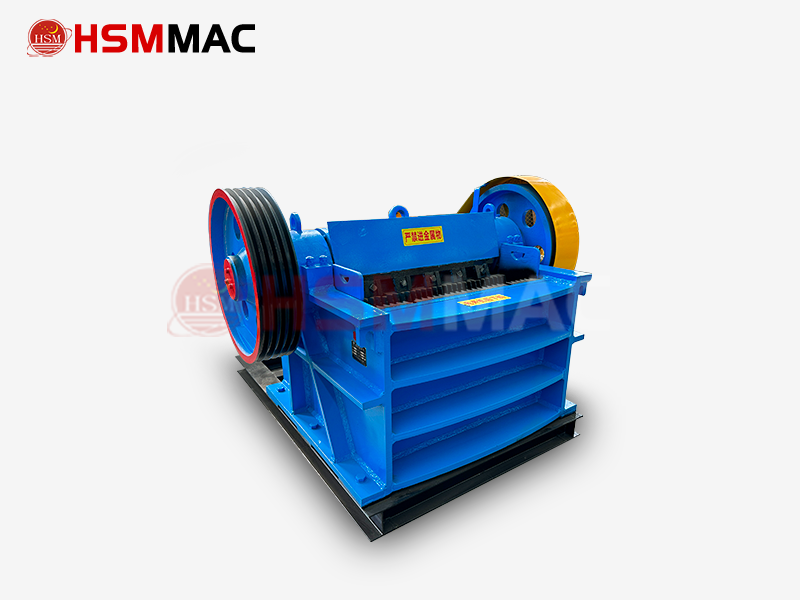

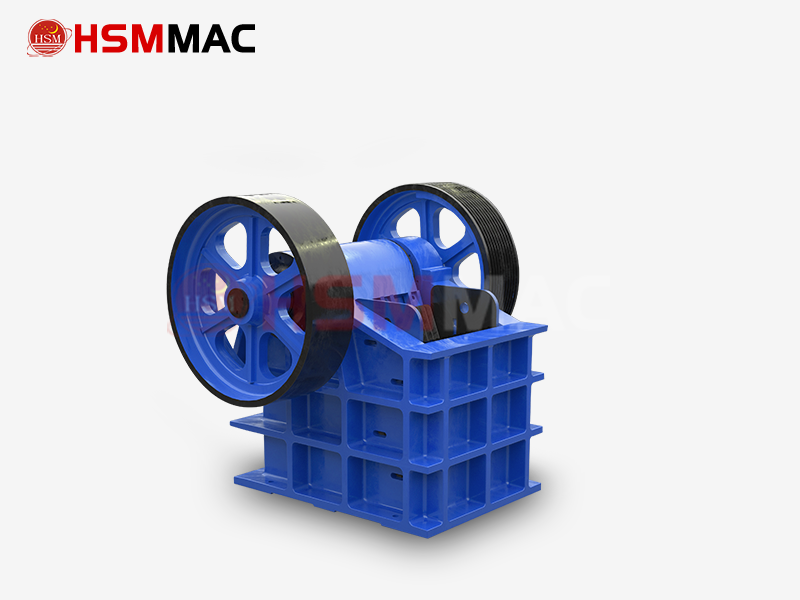
Jaw Crusher

Jaw Crusher
1. Working Principle: Extrusion vs Compression-Shear
Their core difference lies in working principles, which determine crushing effects and material applicability.
Roller Crusher: Relies on relative rotation of parallel rollers to squeeze and grind materials. The process is gentle with little over-crushing.
Jaw Crusher: Uses compression-shear principle. A movable jaw (driven by an eccentric shaft) moves reciprocally against a fixed jaw to crush materials. It has strong crushing force and high ratio.
2. Structural Design: Compact vs Robust
Structural features affect installation, transportation and maintenance.
Roller Crusher: Compact and simple structure, small in size and light in weight, easy to install. Roller surfaces are vulnerable and need regular replacement.
Jaw Crusher: Robust and complex structure, large and heavy, requiring solid foundation for installation. Jaw plates are main vulnerable parts, easy to replace.
3. Applicable Materials: Medium-Soft vs Hard
Crushing force and working mode determine material applicability.
Roller Crusher: Suitable for medium-soft materials (coal, limestone, etc., compressive strength <150MPa). Not for hard/abrasive materials (causes rapid roller wear).
Jaw Crusher: Ideal for primary crushing of hard materials (granite, basalt, etc., compressive strength up to 320MPa). Handles large raw materials well.
4. Product Characteristics: Uniform Particle Size vs Coarse Crushing
Product particle size, shape and uniformity differ significantly.
Roller Crusher: Products have uniform particle size and good shape. Granularity is adjustable via roller gap, suitable for sand making.
Jaw Crusher: Products are coarse and less uniform, often needing secondary crushing. Irregular shape with more needle-like particles, used for primary crushing.
5. Production Capacity and Energy Consumption
Capacity and energy consumption are key economic indicators.
Roller Crusher: Small capacity (1-1000t/h), low energy consumption, suitable for small-medium production lines.
Jaw Crusher: Large capacity (1-10000t/h), high energy consumption, suitable for large-scale production lines.
6. Application Scenarios: Secondary Crushing vs Primary Crushing
Application scenarios are clearly divided based on above differences.
Roller Crusher: Used for secondary/fine crushing (coal-fired power plants, cement plants, sand making, small mines).
Jaw Crusher: Widely used for primary crushing (large mines, highway/railway construction, concrete plants, metallurgy).
Summary: How to Choose?
In short, choose based on project needs:
Choose jaw crusher for hard materials, large raw materials or large-capacity primary crushing;
Choose roller crusher for medium-soft materials, uniform product size or small-capacity secondary/fine crushing.
Also consider equipment cost, maintenance cost and site conditions in practice.